What you need to know about lung cancer
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the lungs, where abnormal cells grow uncontrollably and form tumors. It is one of the most common types of cancer and a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
Awareness and early detection of lung cancer are crucial for improving outcomes and increasing the chances of sccessful treatment. Early detection can lead to more effective treatment options and better prognosis.
Types of Lung Cancer
A. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for approximately 85% of cases. It includes subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. B. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a less common but more aggressive form of lung cancer that tends to spread quickly to other parts of the body. C. Other rare types of lung cancer include carcinoid tumors, sarcomatoid carcinoma, and mesothelioma.
Risk Factors
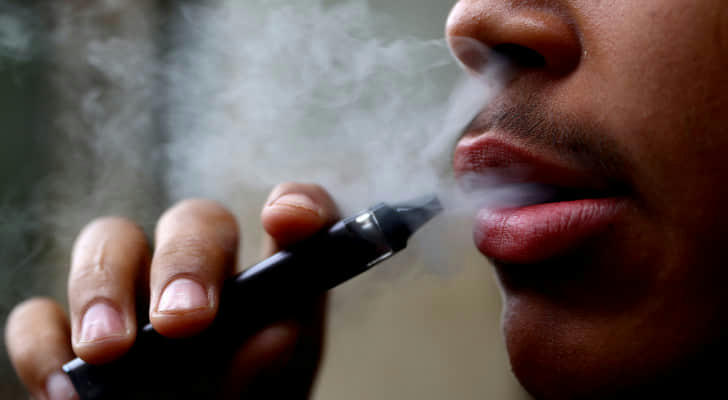

A. Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke are the primary risk factors for developing lung cancer, with cigarette smoking being responsible for the majority of cases.
B. Environmental factors such as exposure to asbestos, radon gas, air pollution, and certain chemicals can also increase the risk of developing lung cancer.
C. Genetic predisposition may play a role in some cases of lung cancer, with certain genetic mutations increasing the susceptibility to the disease.
Symptoms
A. Persistent cough that does not go away or worsens over time.
B. Chest pain that may worsen with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing.
C. Shortness of breath, wheezing, hoarseness, and recurrent respiratory infections.
Diagnosis
A. Imaging tests such as chest X-rays, CT scans, and PET scans can help detect abnormalities in the lungs.
B. Biopsy, where a sample of tissue is taken from the lung for examination under a microscope, is necessary to confirm the presence of cancer.
C. Staging of lung cancer helps determine the extent of the disease and guides treatment decisions.
Treatment Options
A. Surgery may be used to remove the tumor and surrounding tissue in early-stage lung cancer.
B. Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing and spreading.
C. Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells.
D. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are newer treatment options that target specific molecules within cancer cells or boost the body's immune system to fight the cancer.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
A. Factors such as the stage of the cancer, type of lung cancer, overall health of the patient, and response to treatment can affect the prognosis.
B. Survival rates for lung cancer vary depending on the stage at diagnosis, with early-stage cancers having higher survival rates than advanced-stage cancers.
Prevention

Prevention plays a crucial role in the fight against lung cancer, offering a proactive approach to reducing the incidence and impact of this disease. Smoking cessation stands out as the most effective way to prevent lung cancer, as tobacco smoke contains numerous carcinogens that can damage the lungs over time. By quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke, individuals can significantly lower their risk of developing lung cancer.
In addition to smoking cessation, avoiding exposure to other carcinogens such as asbestos, radon, and air pollutants is essential in reducing the risk of lung cancer. Occupational exposure to asbestos, for example, has been linked to an increased risk of developing lung cancer, highlighting the importance of workplace safety measures and regulations. Similarly, radon gas, a naturally occurring radioactive gas found in soil and rocks, can seep into homes and pose a risk to lung health if not properly mitigated.
Furthermore, regular screenings, particularly for individuals at high risk, can play a critical role in early detection and intervention. For those with a history of smoking or other risk factors, such as a family history of lung cancer or exposure to carcinogens, screening tests such as low-dose CT scans can help detect lung cancer at an early and more treatable stage. By prioritizing preventive measures, including smoking cessation, avoiding carcinogenic exposures, and undergoing regular screenings, we can take significant steps towards reducing the burden of lung cancer and improving outcomes for those at risk.
Support and Resources
A. Support groups provide emotional support, information, and resources for individuals and families affected by lung cancer.
B. Counseling services can help patients and their loved ones cope with the emotional and psychological challenges of a lung cancer diagnosis.
C. Informational websites and organizations offer valuable resources, education, and advocacy for lung cancer patients and caregivers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the battle against lung cancer requires a united front and a steadfast commitment to early detection and intervention. By spreading awareness, advocating for lung health, and supporting those affected by this disease, we can make a meaningful impact in reducing its devastating effects. Let us stand together in solidarity, offering hope and compassion to all who are facing the challenges of lung cancer. Together, we can strive for a future where this disease no longer poses a threat to our health and well-being.
